I read something yesterday! To my great delight, and for the first time in my…
The need for occupational hygiene in the workplace

Part of managing any productive working environment is successfully managing occupational hygiene.
Any organisation must manage occupational hygiene, since it is not only a legal obligation, but also a social and moral obligation. It is very important to note that poor management of occupational hygiene can result in low production rates.
Occupational hygiene is well defined in our South African legislation and is promulgated in the Occupational Health and Safety Act (Act 85 of 1993) and in the Mines Health and Safety Act (Act 29 of 1996).
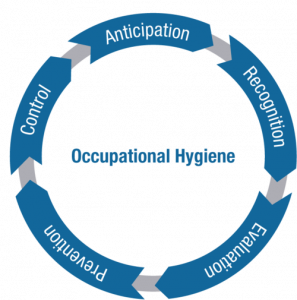 The International Labour Organisation (ILO) estimates that work-related accidents and illnesses annually take 2 million lives and cost the global economy an estimated US$1.25 trillion. This shows just how important occupational hygiene is. Here are a few benefits of managing your working environment effectively:
The International Labour Organisation (ILO) estimates that work-related accidents and illnesses annually take 2 million lives and cost the global economy an estimated US$1.25 trillion. This shows just how important occupational hygiene is. Here are a few benefits of managing your working environment effectively:
- It improves worker health and increases life expectancy
- It reduces the number of people who have to leave employment early
- It lowers social and healthcare costs
- It maximises worker potential
- It allows for an efficient working process and increased productivity
Whilst many of the occupational challenges of the past such as asbestos, lead, crystalline silica and solvents are still with us, albeit in a more controlled environment, these days the range of health risks in the workplace is more varied than ever.
Not only do we recognise chemical hazards but also the health hazards associated with noise, heat or cold, ergonomic stresses, ionising radiation, microwaves, infectious diseases and psychological stress.
An occupational hygienist specialises in identifying health risks in the workplace and advises organisations on how to avoid and resolve them. Working in a variety of locations, including building sites, offices and factories, they promote responsible practice and raise awareness of health and safety issues.
Occupational hygiene is where science and engineering meet the human element of work; it is a specialised discipline within the broad area of occupational health and safety which aims to prevent people injuring themselves or getting ill as a result of their work activities.



